Feel exhausted all the time? Your iron levels might be screaming for attention.
This tiny mineral does massive work inside your body, from carrying oxygen to powering your brain. Yet most of us know almost nothing about how it actually works.
These interesting facts about iron will change that.
You’ll learn what iron does in your body, how to spot deficiency signs early, which foods pack the most iron, and simple tricks to absorb more from every meal.
Plus, some surprising facts that even your doctor might not mention. Let’s get into it.
What Iron Is and Why the Body Needs It?
Iron is a mineral your body cannot make on its own, yet you need it daily to survive.
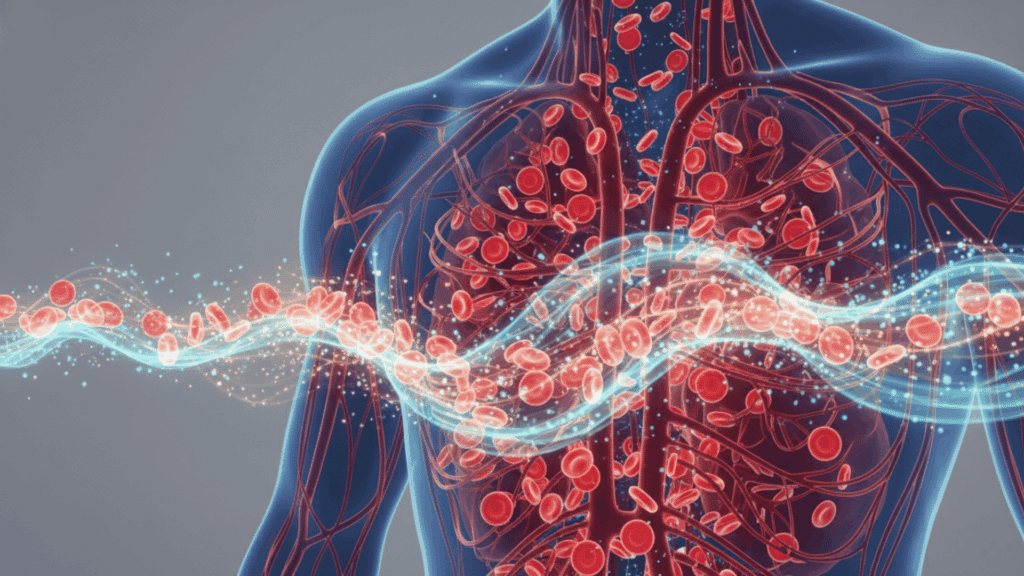
It builds hemoglobin in red blood cells that carries oxygen from your lungs to every tissue, creates myoglobin that stores oxygen in muscles, powers enzymes for energy production, and supports immune function and brain health.
Quick Iron Vocabulary That Clears Confusion:
| Term | What It Is | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Heme Iron | Iron from animal sources | Absorbs easily, your body uses it efficiently |
| Non-Heme Iron | Iron from plant sources | Absorbs less, needs vitamin C to boost uptake |
| Ferritin | Your iron storage protein | Shows how much iron you have saved up |
| Transferrin | Iron delivery system in the blood | Carries iron from storage to cells that need it |
| TIBC | Total iron binding capacity | Measures how much transferrin you have available |
| Transferrin Saturation | Percentage of transferrin carrying iron | Shows if your delivery trucks are full or empty |
| Hepcidin | Iron traffic controller hormone | Decides when to absorb more iron or release stored iron |
18 Interesting Facts About Iron
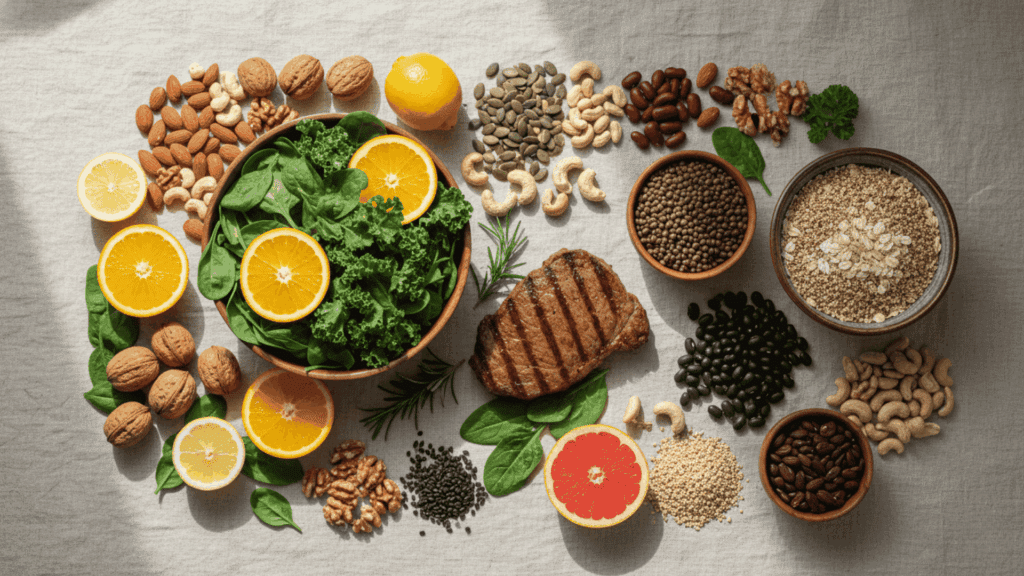

Iron does more than you might expect. These interesting facts about iron show why this mineral matters so much to your health.
-
Iron builds hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that moves oxygen from your lungs to every part of your body.
-
Your body cannot make iron. All the iron you need must come from food or supplements.
-
Most iron lives in red blood cells. Smaller amounts are stored in your muscles, liver, and bone marrow as backup.
-
Iron powers your energy. It helps enzymes turn the food you eat into fuel your cells can actually use.
-
Two types of dietary iron exist. Heme iron comes from animals. Non-heme iron comes from plants.
-
Heme iron absorbs better. Your body takes in heme iron more easily than the plant-based version.
-
Vitamin C boosts iron absorption. Eat oranges, strawberries, or peppers with your iron-rich meal to absorb more iron.
-
Tea and coffee block iron. The tannins in these drinks prevent your body from absorbing iron when you drink them with meals.
-
Iron builds better brains. Kids and teens need enough iron for proper brain development and cognitive function.
-
Low iron is extremely common. Iron deficiency anemia ranks as one of the top nutritional problems in the United States.
-
Your body shows clear warning signs. Fatigue, weakness, pale skin, headaches, and shortness of breath all point to low iron levels.
-
Women need more iron than men. Monthly periods create regular iron loss that requires replacement.
-
Pregnancy doubles iron needs. Growing a baby means making more blood, which demands much more iron.
-
Athletes burn through iron faster. Exercise breaks down red blood cells more quickly and causes iron loss through sweat.
-
Iron protects you from illness. Your immune system relies on iron to fight off infections properly.
-
Cast-iron pans add iron to food. Cooking acidic dishes like tomato sauce in a cast-iron pan slightly increases the iron content.
-
Too much iron causes harm. Taking supplements without a doctor’s guidance can damage your liver and other organs over time.
-
Your body has built-in iron control. A hormone called hepcidin regulates how much iron you absorb and release, keeping levels balanced.
Best Food Sources of Iron
Getting enough iron from food is easier than you think. Here are the top sources that pack the most iron per serving.
| Food Source | Iron Type | Why It Works |
|---|---|---|
| Red meat (beef, lamb) | Heme | Absorbs easily, provides high amounts per serving |
| Chicken liver | Heme | One of the richest iron sources available |
| Oysters and clams | Heme | Loaded with iron and absorbs quickly |
| Sardines and tuna | Heme | Convenient option with good iron content |
| Spinach (cooked) | Non-heme | High iron, when cooked, pairs with vitamin C |
| Lentils and beans | Non-heme | Budget-friendly, versatile, fiber-rich |
| Tofu and tempeh | Non-heme | Great plant-based protein with solid iron |
| Fortified cereals | Non-heme | Easy breakfast option, check labels for amounts |
| Pumpkin seeds | Non-heme | Perfect snack, adds crunch to meals |
| Dark chocolate (70%+) | Non-heme | Tasty treat with surprising iron content |
Signs of Low Iron and Iron Deficiency

Your body sends clear signals when iron runs low. Spotting these signs early helps you fix the problem before it gets worse.
- Constant tiredness and fatigue: You feel exhausted even after a full night’s sleep because your cells aren’t getting enough oxygen.
- Pale skin, nails, and inner eyelids: When hemoglobin drops, your skin loses its healthy pink color and looks washed out.
- Shortness of breath during normal activities: Climbing stairs or walking short distances leaves you breathless since your blood can’t deliver oxygen efficiently.
- Frequent headaches and dizziness: Your brain needs steady oxygen flow, and low iron starves it, causing regular head pain and lightheadedness.
- Cold hands and feet: Poor oxygen circulation means your extremities stay cold even in warm rooms.
- Brittle nails and hair loss: Iron feeds the cells that grow hair and nails, so a deficiency makes them weak and prone to breaking.
How to Absorb More Iron From Meals?
Pair iron-rich foods with vitamin C to boost absorption by up to 300%. Add citrus fruits, tomatoes, or bell peppers to your meal.
Avoid drinking tea, coffee, or milk with iron-rich meals, as tannins and calcium can block iron absorption. Cook in cast-iron pans to add extra iron to your food.
Eat heme iron sources (meat, fish, poultry) alongside non-heme iron sources (beans, spinach, lentils) because heme iron helps your body absorb the plant-based iron better.
Space out calcium supplements and antacids by at least two hours from iron-rich meals.
Final Take
Iron keeps you alive, alert, and full of energy. These interesting facts about iron show just how much this mineral affects your daily life.
From building healthy blood to powering your brain, iron works behind the scenes every single day. Know the signs of low iron. Choose the right foods. Pair them smart to absorb more.
Your body will thank you with improved energy, sharper focus, and better overall health.
Got questions about your iron levels? Talk to your doctor about getting tested. Drop a comment below sharing your favorite iron-rich meal or any tips that worked for you.